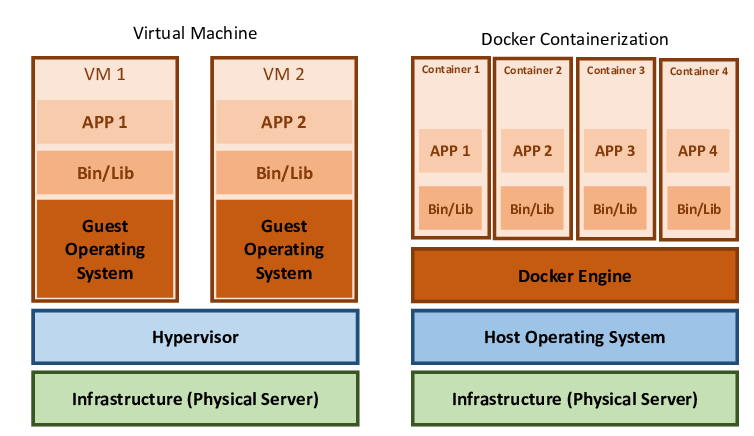
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) encompasses a suite of principles and tools aimed at facilitating the seamless delivery of software updates to users. By incorporating automation into software development workflows, CI/CD ensures that changes are rolled out promptly, consistently, and securely. This article delves into the necessity and significance of implementing a CI/CD pipeline, offering insights into optimal practices for streamlining the software delivery process.
What is CI & CD?
Continuous integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge their code changes into a shared repository, typically multiple times a day. Each integration triggers an automated build and automated tests to detect integration errors quickly. CI helps teams catch and fix bugs early in the development process, ensuring that the software remains stable and functional as new features are added.
Continuous deployment (CD), on the other hand, is the process of automatically deploying code changes to production environments after passing through the CI process. CD enables teams to automate the deployment process, allowing new code changes to be released to users rapidly and consistently. By automating deployment, CD reduces the manual effort required to release updates and helps ensure that changes are delivered to users in a timely and reliable manner.

Benefits of Implementing a CI/CD Pipeline
Early Bug Detection: CI/CD pipelines emphasize thorough testing, which helps identify and fix bugs, errors, or vulnerabilities in the code at an early stage. Automated testing increases test coverage and reduces human error, resulting in higher-quality software with fewer issues, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Quick Time to Market: By automating manual tasks like code builds, tests, and deployments, CI/CD pipelines significantly reduce the time developers spend on these tasks. This frees up more time for focusing on adding new features and enhancements, enabling faster delivery of new features to clients and customers.
Enhanced Collaboration and Transparency: Unlike traditional workflows where different departments work in isolation, CI/CD pipelines promote collaboration among development and operations teams. Information like code quality metrics, build results, and errors is readily available, fostering transparency and visibility across teams. This frequent communication ensures alignment with project goals and minimizes miscommunications.
Adaptability and Scalability: CI/CD pipelines can be tailored to meet the unique needs of various software development projects. Customizing the pipeline to suit different project requirements makes it more flexible than traditional workflows. Additionally, scaling the pipeline up or down based on project demands is easier with CI/CD pipelines.
Cost Efficiency: Manual testing and deployment in traditional workflows incur significant time and financial investments. CI/CD pipelines automate much of this process, reducing both the time and financial costs associated with manual testing and deployment. This cost-saving benefit makes CI/CD pipelines a valuable asset for any development team.
Best Practices of CI/CD
Automate Everything: One of the fundamental best practices of CI/CD is to automate every aspect of the software delivery process, including code compilation, testing, and deployment. Automation ensures consistency, repeatability, and speed in the delivery pipeline, reducing manual errors and accelerating the overall development cycle.
Version Control: Effective version control, such as using Git, is crucial for CI/CD pipelines. It enables teams to manage changes to the codebase, collaborate efficiently, and rollback to previous versions if necessary. By maintaining a clear history of changes, version control enhances transparency, accountability, and the ability to trace issues.
Continuous Testing: Continuous testing is a cornerstone of CI/CD best practices. Implementing automated tests at every stage of the pipeline, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests, helps detect bugs early, validate changes, and ensure the overall quality of the software. Comprehensive test coverage ensures that any issues are identified and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of defects in production.
Parallel Execution: Parallel execution involves running multiple tasks simultaneously within the CI/CD pipeline, optimizing resource utilization and reducing overall build times. By parallelizing tasks such as test suites or deployment processes, teams can achieve faster feedback loops and accelerate the delivery of features to users. Parallel execution also enhances scalability, enabling pipelines to handle larger workloads efficiently.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback: Continuous monitoring and feedback provide valuable insights into the performance and health of applications deployed through the CI/CD pipeline. Integrating monitoring tools and metrics allows teams to identify bottlenecks, track key performance indicators, and proactively address issues in real-time. Regular feedback loops enable continuous improvement, driving iterative enhancements to the delivery process and the overall software product.
A Typical CI/CD Pipeline
Commencing on a software development journey entails navigating through a maze of processes, from code creation to deployment. To simplify this intricate path, Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines serve as indispensable tools. Let’s delve into a blueprint of a typical CI/CD pipeline, designed to streamline the software development lifecycle. (Imge Credit: Jason’s Blog-Beningo)
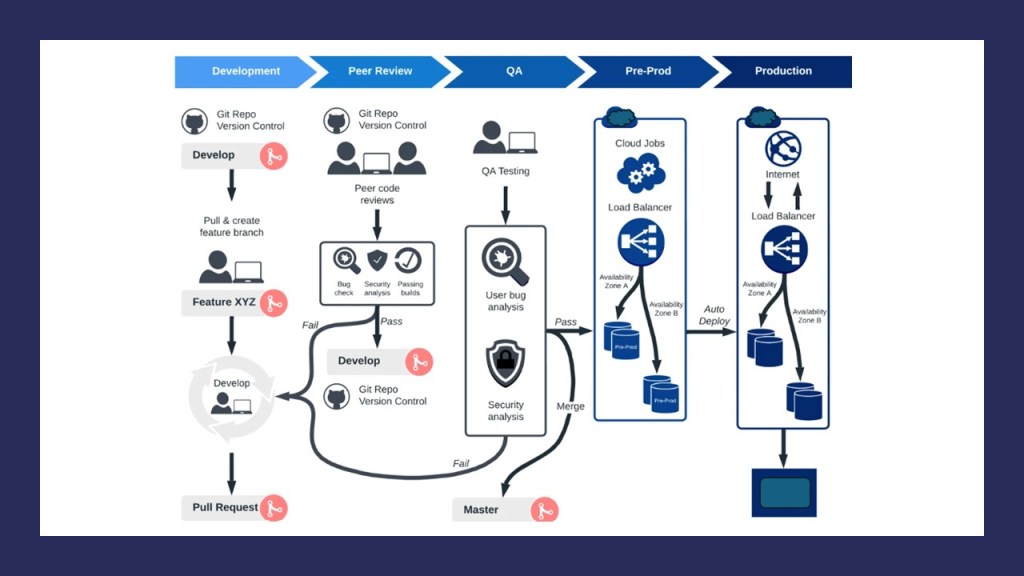
- Code Management: The journey begins with source code management, where all project packages and dependencies find their home. Establishing a structured review mechanism ensures code integrity, with designated reviewers approving changes via pull requests. Building upon this foundation, the code undergoes compilation and unit testing, crucial for early issue detection and ensuring application functionality.
- Testing Environment: Transitioning to the testing environment, integration tests play a pivotal role in validating API behavior and adherence to business rules. This phase ensures that APIs fulfill expected functionalities, such as order creation and adherence to predefined constraints. Toggle switches facilitate flexible stage control, enabling seamless progression through the deployment pipeline.
- 1-Box Deployment: Mitigating deployment risks, the 1-box deployment strategy facilitates controlled testing with a fraction of production traffic. This precautionary measure minimizes the impact of potential issues, allowing swift rollback in case of anomalies. Rollback alarms and bake periods further fortify the deployment process, ensuring stability and resilience.
- Production Environment: Finally, the journey culminates in the production environment, where the full deployment unfolds. Here, the same safeguards and monitoring mechanisms are in place to uphold performance standards and swiftly address deviations. With a systematic approach and rigorous testing at each stage, the CI/CD pipeline paves the way for smoother, faster, and more reliable software development.
Conclusion
In summary, adopting CI/CD transforms software development by promoting teamwork, improving productivity, and providing smooth user interactions. Following best practices and using automation empower teams to manage deployment challenges effectively, leading to successful software launches and ongoing improvements.