GraphQL An Overview
GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for executing those queries with existing data. It was developed by Facebook in 2012 and released as an open-source project in 2015. Unlike traditional REST APIs, which expose a fixed set of endpoints that return predetermined data structures, GraphQL allows clients to request only the data they need, in the shape they need it, using a single endpoint. This flexibility empowers frontend developers to fetch precisely the data required for their UI components, eliminating over-fetching and under-fetching of data.

GraphQL operates on a type system, where each data type represents a component of the API schema. Clients can query these types to fetch nested data and even perform mutations to modify the data. This paradigm shift in API design offers several advantages, including improved performance due to reduced network overhead, simplified client-server communication, and enhanced developer productivity through self-documenting APIs. Major companies like GitHub, Shopify, and Airbnb have adopted GraphQL to streamline their API development and provide efficient data access to their applications.
Features & Functionality of GraphQL
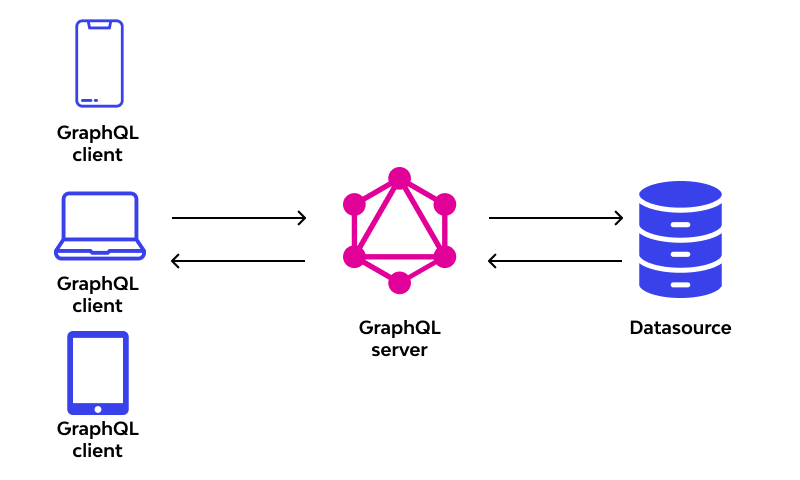
One of the main features of GraphQL is its strongly-typed schema. The schema defines the capabilities of the API and serves as a contract between the client and server. It consists of types, which represent the data structures exposed by the API, along with fields, which specify the properties of each type. Additionally, GraphQL supports queries, mutations, and subscriptions, providing flexible mechanisms for reading, writing, and subscribing to data. Queries allow clients to fetch data from the server, mutations enable clients to modify data, and subscriptions enable real-time data updates. Another key feature is introspection, which allows clients to query the schema itself to discover available types and fields, enabling powerful tooling and documentation generation. Overall, GraphQL’s combination of flexibility, type-safety, and introspection empowers developers to build efficient and self-documenting APIs.
GraphQL operates on a type system, where each data type represents a component of the API schema. Clients can query these types to fetch nested data and even perform mutations to modify the data. This paradigm shift in API design offers several advantages, including improved performance due to reduced network overhead, simplified client-server communication, and enhanced developer productivity through self-documenting APIs. Major companies like GitHub, Shopify, and Airbnb have adopted GraphQL to streamline their API development and provide efficient data access to their applications.
GraphQL operates on a simple premise: clients specify the exact data they need, and servers respond with precisely that data. This interaction occurs through a single endpoint, typically /graphql, which accepts incoming queries, mutations, and subscriptions. When a client sends a GraphQL request, it includes a query, which describes the data it needs, along with any variables required for the query. The server then executes the query against its schema, resolving each field to retrieve the requested data. Once all fields are resolved, the server returns a JSON response containing the requested data.
Utilization, Benefits, and Drawbacks of GraphQL
Usage
GraphQL is particularly useful in scenarios where there is a need for flexible data fetching, real-time updates, and efficient network communication. Here are some situations where GraphQL shines:
- Complex Data Requirements: When applications require complex data fetching scenarios where traditional REST APIs might lead to over-fetching or under-fetching of data, GraphQL allows clients to specify precisely the data they need, minimizing unnecessary data transfer.
- Real-time Updates: Applications that require real-time updates, such as social media feeds, chat applications, or live sports scores, can benefit from GraphQL subscriptions. Subscriptions enable clients to subscribe to specific data changes and receive updates in real-time.
- Multiple Clients: In scenarios where multiple clients with different data requirements need to interact with the same backend API, GraphQL’s flexibility allows each client to request only the data it needs, reducing over-fetching and improving performance.
- Rapid Development: GraphQL simplifies frontend development by providing a single endpoint for data fetching and updates. This can streamline the development process, especially for teams building modern, interactive web and mobile applications.
Benefits
Advantages of GraphQL:
- Efficient Data Fetching: Clients can request only the data they need, reducing over-fetching and minimizing network payloads.
- Strongly-Typed Schema: GraphQL’s schema definition language provides type safety and documentation, enabling better collaboration between frontend and backend developers.
- Real-time Updates: GraphQL subscriptions enable real-time data updates, making it suitable for applications requiring live data feeds.
- Tooling and Ecosystem: GraphQL has a rich ecosystem of tools and libraries for development, testing, and performance monitoring, enhancing developer productivity.
- Backward Compatibility: GraphQL APIs are backward-compatible by design, allowing developers to evolve APIs without breaking existing clients.
Drawbacks
Disadvantages of GraphQL:
- Complexity: Implementing a GraphQL server requires a deeper understanding of GraphQL concepts and best practices compared to traditional REST APIs.
- Caching: GraphQL does not provide built-in caching mechanisms, which may require additional effort to implement caching strategies effectively.
- Over-fetching: In some cases, GraphQL queries may still result in over-fetching of data if not carefully designed, leading to performance issues.
- Learning Curve: Developers unfamiliar with GraphQL may face a learning curve when adopting the technology, especially when transitioning from RESTful architectures.
- Error Handling: Error handling in GraphQL can be challenging, especially when dealing with nested data fetching and mutations. Proper error handling strategies are crucial for maintaining a robust API.
Rest Vs GraphQL
REST (Representational State Transfer) and GraphQL are both API design architectures used for building web APIs, but they have different approaches and characteristics. Here’s a comparison between REST and GraphQL along with examples to illustrate the differences
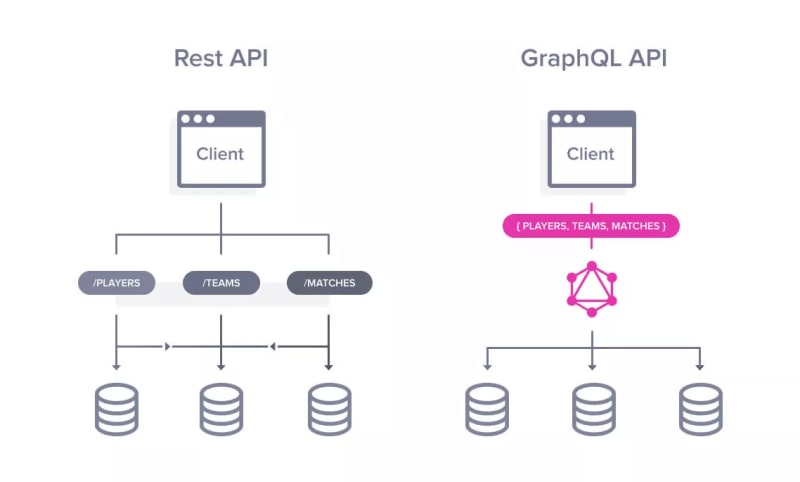
Data Fetching
GraphQL: With GraphQL, clients can request precisely the data they need using a single endpoint. Clients send queries specifying the structure of the data they require, and the server responds with JSON objects matching the requested structure. This allows clients to avoid over-fetching or under-fetching data.
REST: In RESTful APIs, endpoints represent resources, and clients typically make requests to specific endpoints to fetch or manipulate data. Each endpoint corresponds to a specific resource or collection of resources, and the server responds with the entire resource or a subset of it.
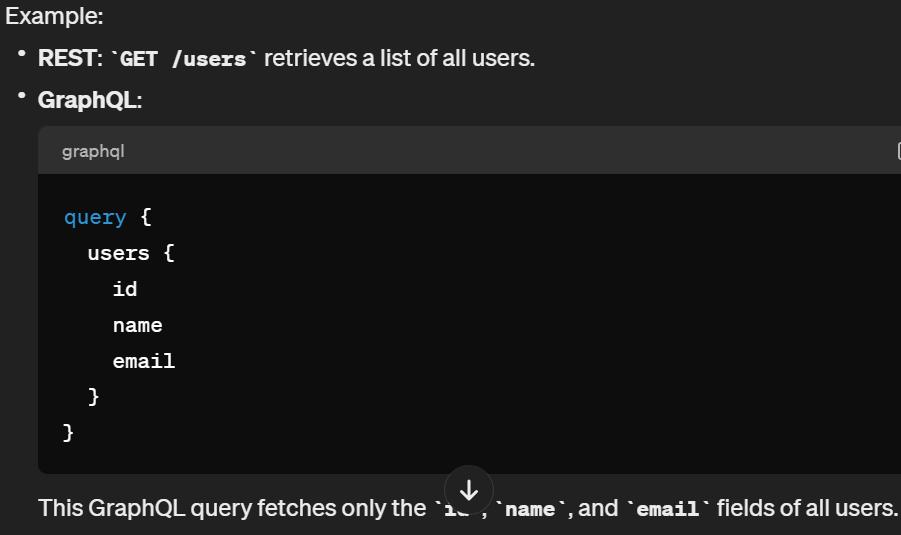
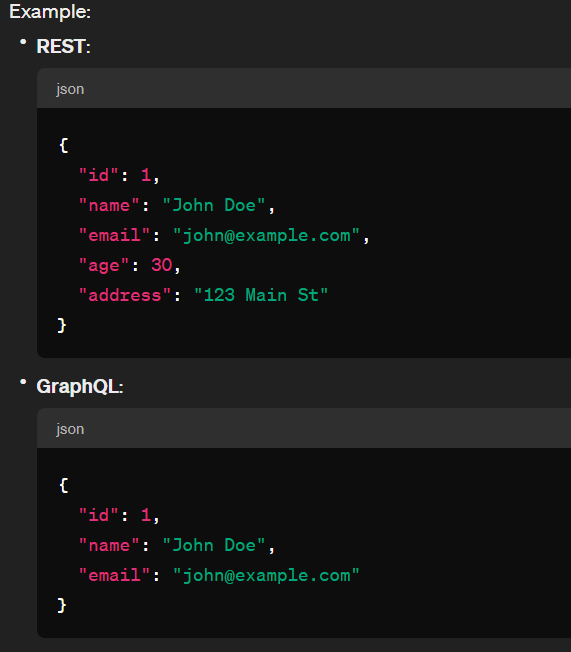
Response Structure
GraphQL: With GraphQL, clients specify the structure of the response in their queries, allowing them to request only the fields they need. This results in more efficient data transfer and reduces the likelihood of over-fetching.
REST: In RESTful APIs, the server defines the structure of the response, and clients receive the same structure for each request to a specific endpoint. This can lead to over-fetching of data if the client doesn’t need all the information provided by the server.
Multiple Requests
GraphQL: With GraphQL, clients can request nested data in a single query, reducing the need for multiple round trips to the server and minimizing over-fetching and under-fetching.
REST: In RESTful APIs, clients often need to make multiple requests to different endpoints to fetch related data, leading to issues like over-fetching or requiring multiple round trips.
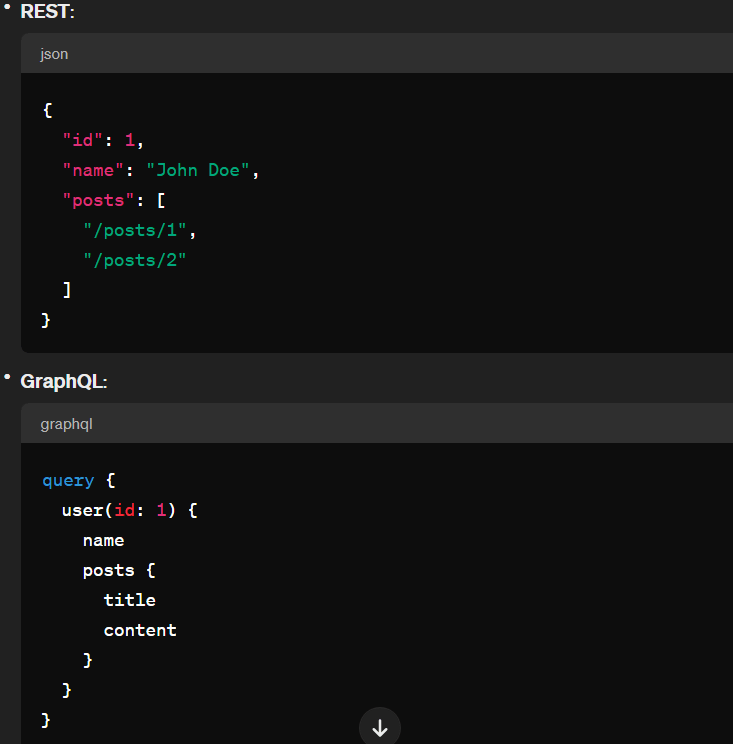
In summary, while RESTful APIs follow a predefined structure and require multiple endpoints for different data requirements, GraphQL allows clients to request precisely the data they need in a single query, resulting in more efficient data transfer and reducing the likelihood of over-fetching or under-fetching data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GraphQL presents a compelling solution for modern API development with its flexibility, real-time updates, and efficient data fetching capabilities. By allowing clients to request precisely the data they need in a single query, GraphQL minimizes over-fetching and under-fetching, leading to improved performance and reduced network overhead. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that adopting GraphQL introduces complexity, especially in managing schema evolution, caching, and authorization. Therefore, organizations must carefully weigh the benefits against the challenges and evaluate whether GraphQL aligns with their project requirements and constraints before implementation.
