Cloud Computing and Edge Computing are two paradigms that address the processing and storage of data in different ways, each with its own set of advantages and use cases.
Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing involves the centralized processing and storage of data in remote servers, commonly referred to as the “cloud.” This model allows users to access computing resources and services over the internet. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Cloud computing is well-suited for applications with high computational needs, such as complex data analysis, machine learning, and large-scale data storage. It provides scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness by allowing users to pay only for the resources they use.
Edge Computing: Edge Computing, on the other hand, involves processing data closer to the source of generation, typically at or near the edge of the network. This reduces latency and enhances real-time processing, making it ideal for applications where immediate data analysis is crucial, like IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. Edge computing minimizes the need to transmit large volumes of data to centralized cloud servers, leading to faster response times and improved efficiency.
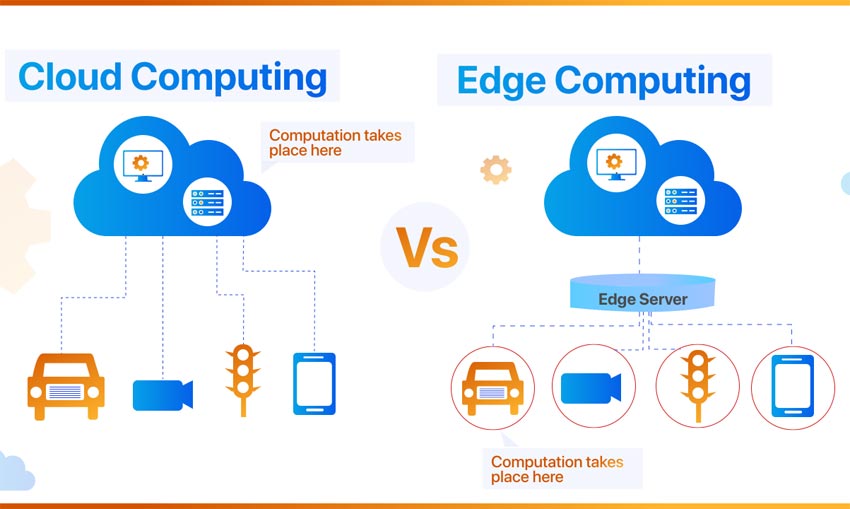
Data Analytics in Both Models: In the context of data analytics, Cloud Computing is often leveraged for large-scale, batch processing tasks. For instance, analyzing massive datasets or training machine learning models might be more efficiently done in the cloud. Edge Computing, on the other hand, is advantageous for real-time analytics, where data needs to be processed instantly, like monitoring and responding to sensor data in smart cities.
Importance of Knowing the Difference: Understanding the difference between Cloud and Edge Computing is crucial for businesses and developers when designing their technology infrastructure. It helps in selecting the most suitable architecture based on the specific requirements of the application. While cloud computing offers centralized power and resources, edge computing provides agility and reduced latency. Striking the right balance or even combining both approaches, known as edge-to-cloud architecture, is becoming increasingly important as technology advances.
Leaders in Edge Computing: Prominent players in the edge computing space include Aarna Networks, ADLINK, EdgeConneX. ClearBlade, Dell Technologies, and Cisco.
Leaders in Cloud Computing: Major players in the cloud computing industry are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM, Oracle, and Alibaba.
Being aware of these distinctions empowers organizations to make informed decisions about where to process and store their data, optimizing performance and efficiency based on their specific needs and use cases.

One Reply to “”